Paper | Artificial Intelligence Ethics System: Infrastructure And Key Issues
Paper | Artificial Intelligence Ethics System: Infrastructure And Key Issues
Abstract: A basic consensus has been reached on the discussion of the ethical norms of artificial intelligence across the globe. On this basis, this paper further studies four key issues: the operating mechanism of the artificial intelligence ethics system, the scenario implementation of artificial intelligence ethics standards, the prediction and identification of artificial intelligence ethics risks, and the comprehensive innovation of artificial intelligence ethics on major social issues support mechanism problem. These questions go beyond the scope of artificial intelligence ethical standards, but they are necessary to answer a complete and effective artificial intelligence ethical system. The main contribution of this article is to put forward a set of suggestions on these four issues.
Artificial Intelligence Ethics System: Infrastructure and Key Issues
Chen Xiaoping


Abstract: A basic consensus has been reached on the discussion of the ethical norms of artificial intelligence across the globe. On this basis, this paper further studies four key issues: the operating mechanism of the artificial intelligence ethics system, the scenario implementation of artificial intelligence ethics standards, the prediction and identification of artificial intelligence ethics risks, and the comprehensive innovation of artificial intelligence ethics on major social issues support mechanism problem. These questions go beyond the scope of artificial intelligence ethical standards, but they are necessary to answer a complete and effective artificial intelligence ethical system. The main contribution of this article is to put forward a set of suggestions on these four issues.
Keywords: Ethical innovation in risk prediction of artificial intelligence ethical system ethics
of : and key
CHEN


: On the basis of on or so far in the world, four key on of AI will be in this paper: of AI , the of AI in real-world , and of risks of AI , and of major by the AI . These go the realm of AI , while they must be in order to a and of AI . A plan for these is as the main of this paper.
With the important progress brought about by the third wave of artificial intelligence, the challenges of artificial intelligence ethics have become a focus of common attention at home and abroad. Some organizations and institutions have conducted seminars on related topics and issued a number of suggestions on artificial intelligence ethics guidelines. . The China Artificial Intelligence Society attaches great importance to the issue of artificial intelligence ethics and began to form an artificial intelligence ethics committee in mid-2018. At the 2019 Global Artificial Intelligence Technology Conference, the "Artificial Intelligence Ethics from a Global Perspective" forum was held on May 26, and the issue of planning for the artificial intelligence ethics system was raised for the first time in the international community, which means that the construction of artificial intelligence ethics has begun to enter the third At the stage, research on key issues in the artificial intelligence ethics system has been put on the agenda. As Academician Li Deyi, Chairman of the Chinese Society of Artificial Intelligence, pointed out in his speech at the forum, this forum is of milestone significance.
1. Construction of artificial intelligence ethics: from ethical standards to ethical systems
The construction of artificial intelligence ethics has gone through two stages. The first stage is a discussion on the necessity of artificial intelligence ethics. From a professional perspective, American scholars such as Yale University took the lead and attracted widespread attention internationally; from a broader background, Yuval Harari's " A Brief History of Humanity played an important role in promoting it. The second stage is the discussion of the ethical norms of artificial intelligence. The EU is ahead, and China and some other countries are also actively participating.
In the second phase, the EU Senior Expert Group on Artificial Intelligence Ethics proposed seven guidelines for Artificial Intelligence Ethics [1], including: ensuring human initiative and supervision, ensuring technical robustness and security, strengthening privacy and data management, and ensuring that Transparency, maintain diversity, non-discrimination and fairness in the use of artificial intelligence systems, enhance social welfare, and strengthen accountability. The Artificial Intelligence and Security Project Team of Tsinghua University in my country proposed 6 guidelines [2]: welfare principle, security principle, sharing principle, peace principle, rule of law principle, and cooperation principle. According to incomplete statistics [3-15], more than 40 institutions or organizations have proposed their respective AI ethical guidelines. Overall, all of these guidelines are basically consistent.
Therefore, this article believes that the discussion stage of artificial intelligence ethical standards has reached a consensus and has basically ended. Based on these consensuses, the construction of artificial intelligence ethics needs to enter the third stage, namely the discussion of the artificial intelligence ethics system.
So, what is the difference between the "artificial intelligence ethics system" and the "artificial intelligence ethics code"? What is the necessity and urgency of developing a discussion on the artificial intelligence ethics system? I believe that the following four key questions cannot be answered by ethical standards and cannot be avoided by the construction of the artificial intelligence ethical system. Without solving these problems, it is impossible to establish a complete and effective artificial intelligence ethics system.
First, the operation mechanism of the artificial intelligence ethical system. No ethical norms can be implemented by themselves. They must be implemented by a series of mutually coordinated operating mechanisms in the ethical system. This is just like no matter how well the legal provisions are formulated, they cannot be implemented by themselves. They must be implemented in a complete legal system, which is composed of mechanisms such as legislation, judicial, and law enforcement. Without the support of a complete legal system, there will inevitably be a problem of not following the law. Of course, the ethical system and the legal system are very different. It is impossible to completely copy the "template" of the legal system, so it is necessary to discuss the artificial intelligence ethical system, especially the discussion of the operating mechanism.
Second, the scenario implementation of artificial intelligence ethical standards. Most of the ethical standards of artificial intelligence that have been proposed are principles that reflect universal values. When applying these criteria to specific actual scenarios, they need to be refined into operational specific regulations, otherwise they will inevitably remain at the level of slogans and cannot be implemented. For example, unmanned driving can have two essentially different application scenarios. One is a completely unmanned transportation system. There are only driverless cars in this transportation system and no manned cars. Pedestrians must strictly abide by rules that are completely different from ordinary road traffic. Another application scenario is a hybrid traffic system, where driverless cars and driverless cars exist at the same time, and pedestrians comply with ordinary road traffic rules. Although these two types of transportation systems are both driverless application scenarios, the technical and ethical risks they face are very different. In hybrid transportation systems, artificial intelligence technology faces challenges of greater difficulty and complexity, and most of the most difficult challenges do not exist in driverless transportation systems. Therefore, in the AI ethical system, very different regulatory regulations need to be formulated for the two transportation systems, even if the two transportation systems comply with the same AI ethical guidelines.
Third, the issue of predicting and discriminating the ethical risks of artificial intelligence. All civil aviation authorities in the world have stipulated a list of prohibited items, and are forced to implement boarding security checks to check whether passengers and flight attendants have carried prohibited items. In the artificial intelligence ethics system, there is also a need for some kind of "banned items" corresponding to the "list of prohibited items" in order to carry out targeted risk supervision and control. Obviously, the ethical standards of artificial intelligence are just some principles and do not include the "list of prohibited items" of artificial intelligence. For example, the "safety principle" cannot specifically point out which artificial intelligence technologies are unsafe, and the "fairness principle" cannot specifically point out which Artificial intelligence technology is unfair. At the same time, artificial intelligence is in the process of continuous development, and it is impossible to list a complete "list of prohibited items" once and for all. Therefore, a normalized mechanism can only be established in the artificial intelligence ethics system, which can predict and determine what risks any artificial intelligence technology has, how high the risks, whether it should be disabled, etc. This mechanism did not exist in the past, and this is a completely new issue facing mankind.
Fourth, the driving mechanism for comprehensive innovation in major social issues. The basic focus of ethics revolves around "correct and wrong behavior" [16-17]; that is, ethics does not only care about "not doing wrong things", but also about "doing good things". However, in the discussion on artificial intelligence ethics so far, the risk prevention side has been widely paid attention to and widely discussed, while the side that promotes social progress and economic development has not been paid enough attention, which has become the biggest shortcoming in the construction of the artificial intelligence ethics system. There is a view that the issue of promoting economic development and social progress should and has been undertaken by artificial intelligence research and industrialization, and there is no need for the intervention of artificial intelligence ethics. This view is not in line with the reality of today's society and future development trends. For example, according to statistics from the Ministry of Civil Affairs and other departments, 250 million families in China need housekeeping services, while there are less than 17 million domestic service personnel. According to a 2016 survey by the China Office of Aging, the total number of disabled and semi-disabled elderly people in China has reached 40 million, and an increase of 8 million per year. Similar problems also exist to varying degrees in developed countries. At present, it is difficult to find effective solutions to these problems, because the main driving mechanism of existing science and technology and industrial innovation () is commercialization, and the effectiveness of commercialization mechanisms to deal with social problems such as aging is seriously insufficient. In the future, this situation will be more and more serious. Becoming more and more serious. Therefore, it is necessary to add a new comprehensive innovation mechanism outside the commercialization mechanism, that is, ethical innovation with the help of artificial intelligence technology.
2 The infrastructure of the artificial intelligence ethics system
An infrastructure of the artificial intelligence ethics system is shown in Figure 1. This architecture does not contain all the contents of the artificial intelligence ethics system, but focuses on answering the four key questions pointed out above.
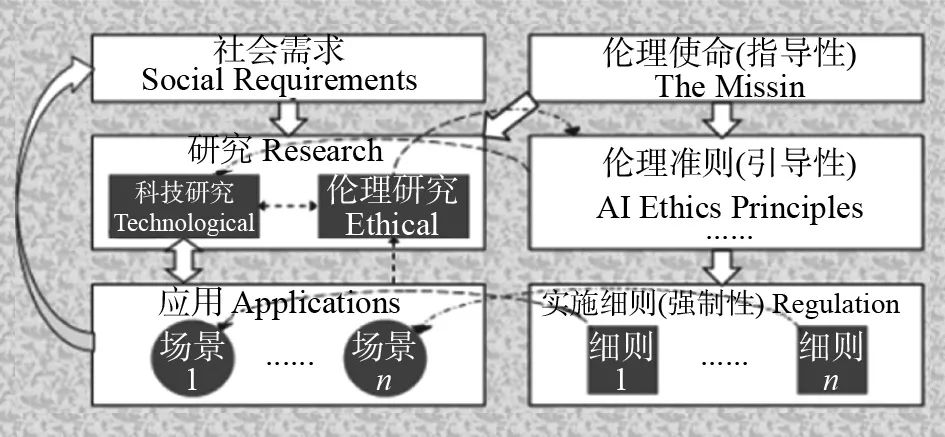
Figure 1 Artificial Intelligence Ethical Mechanism Architecture
Fig. 1A of the AI
According to popular view, the artificial intelligence innovation ecosystem includes three main links, namely "social demand", "research" and "application", which form a closed loop of circular evolution, that is, demand-driven research, and mature research results are realized through commercialization. Application, and practical applications can trigger new demands. This closed loop is the object of the artificial intelligence ethics system. After the establishment of the artificial intelligence ethics system, the composition and operating mechanism of the entire artificial intelligence ecosystem will also be greatly changed and upgraded.
Artificial intelligence ethics play a role through three levels: the upper level is the basic mission of artificial intelligence ethics; the middle level is the ethical norms of artificial intelligence; and the lower level is the operational supervision and governance regulations for specific application scenarios.
In the infrastructure of the artificial intelligence ethics system shown in Figure 1, we define the basic mission of artificial intelligence ethics as "providing ethical support for improving human well-being and the harmonious coexistence of all things." This mission itself is also an ethical standard, but compared with other criteria, its value is greater universality and stability. Its connotation summarizes the connotation of other ethical standards, while other ethical standards may not necessarily summarize the connotation of the basic mission. Therefore, the basic mission can be used to guide the research and application of artificial intelligence, as well as the formulation, improvement and improvement of middle-level ethical standards, while other ethical standards may not be or may not be used to guide ethical research. In addition, research on the ethical nature of artificial intelligence is unlikely to change the connotation of the basic mission, but it can affect and change the connotation of other ethical norms. In short, the basic mission of artificial intelligence ethics can be regarded as the "criterion of ethical norms", that is, the basic values of artificial intelligence.
The ethical norms of the middle level are those value principles that have been reached in the second stage of the construction of artificial intelligence ethics. These ethical standards are a concrete manifestation of the basic mission and provide guidance for the formulation of implementation rules and scientific and technological research practice.
In order to implement ethical standards into specific application scenarios, targeted, mandatory and operational implementation details need to be formulated, namely a complete set of supervision and governance regulations. Each application scenario is constrained by a set of corresponding regulations, and different application scenarios can have different regulations. For a specific application scenario, a set of regulations often includes the following specific requirements and specifications: product standards (enterprise standards), technical standards (group standards/national standards/international standards), industry regulations, industrial policies, regulations, etc. These different aspects of regulations are formulated and supervised by different agencies, including enterprises, standardized organizations, industry organizations, government departments and legal institutions, and there is a complex relationship between these regulations. For example, the indicators of product standards formulated by enterprises shall not be lower than the indicators of technical standards formulated by standardization organizations. Product standards and technical standards are aimed at a specific category of products or services, while industry regulations and industrial policies are aimed at the entire industry, so they are complementary. Regulations are provisions made at the legal level, with the highest mandatory and authoritative nature, and are usually not targeted at specific products and services, or even not targeted at specific industries.
From the composition of the provisions as ethical implementation rules, it can be seen that the construction of artificial intelligence ethics cannot be completed by experts in a certain field, but must involve a series of relevant parties, from enterprises, universities and scientific research institutions, standardization organizations, industry organizations, Government agencies to legal departments require mutual coordination and joint efforts of all these stakeholders. In the coordination of relevant parties, it is necessary to not only abide by common ethical norms, but also by the agreements of the ethical system infrastructure for their respective roles.
3. The risk prediction and discrimination mechanism of artificial intelligence
A necessary prerequisite for realizing the basic mission of artificial intelligence ethics is to ensure the ethical bottom line of artificial intelligence, that is, to ensure that the risks of artificial intelligence research and application are within a controllable range. Overall, artificial intelligence has the following three risks. First, technology misuse: Due to the inadequate maturity, inhumanity or lack of sufficient ethical constraints, it brings direct damage to users, such as data privacy issues, security issues and fairness issues. Second, technology is out of control: that is, humans lose control of artificial intelligence technology and have serious consequences. For example, many people are now worried that in the future, artificial intelligence will surpass human intelligence and capabilities, and will dominate human beings. Third, application out of control: the widespread application of artificial intelligence technology in certain industries has brought serious negative social effects, such as causing many people to lose their jobs.
At present, there are no relevant institutions and sufficient research forces around the world, which can predict and judge these three risks. Therefore, it is necessary to add a new research model and department in the artificial intelligence innovation ecosystem - artificial intelligence ethical research. One of the core functions of this research is to assume the prediction and judgment of three risks, that is, to be an artificial intelligence Guardian of the bottom line of risk. Therefore, in the future artificial intelligence innovation ecosystem, "research" will be divided into two relatively independent departments, one is the traditional scientific and technological research/technical research department, and the other is the ethical research department, where there is a mutual support relationship between them. .
There is an essential difference between research on risk prediction and discrimination of artificial intelligence and traditional scientific and technological research. Research in technical disciplines has always been aimed at "potential applications", while research in natural sciences aims at "seeking knowledge". The basic function of research on risk prediction and discrimination of artificial intelligence is to explore the risks of a certain technology through scientific means based on ethical standards. and its severity, thus providing a reliable basis for whether the technology should be disabled. Therefore, the research on risk prediction discrimination is mainly aimed at "potential ban". It can be seen from this that it is absolutely necessary to establish an artificial intelligence ethics research department. In Figure 1, there is a closed loop from ethical research to ethical standards, to implementation rules, to application scenarios and then to ethical research. This closed loop reflects the role of artificial intelligence ethical research in the entire innovation ecosystem.
For three risks, the main tasks and necessities of the research on artificial intelligence risk prediction and discrimination are summarized as follows.
Regarding the first ethical risk, in fact, it has existed in the application of existing artificial intelligence and other technologies. The severity of this situation has been generally underestimated and has not been effectively supervised and controlled. Therefore, in response to ethical issues such as data privacy, security, and fairness, it is urgent to strengthen the construction of the ethical system of artificial intelligence and related technologies, strengthen the construction of professional teams, strengthen the research on specific ethical issues, and set higher standards of relevant regulations. Implementing effective supervision and governance should become the key tasks of current research and governance of artificial intelligence ethics.
The second risk is not very urgent in the near future, but the long-term severity must not be underestimated. Traditional technologies are not autonomous, while artificial intelligence can be completely autonomous. Complete autonomy means that artificial intelligence can realize the perception, decision-making and action of complex tasks in the real world completely independent of humans. Some analysts believe that once a completely autonomous artificial intelligence system with a human self-awareness is developed, it will independently reproduce and evolve itself, and break through any ethical norms and human control [18]. If this is true, allowing such an artificial intelligence system to be developed means that humans will be dominated by artificial intelligence, which means that any artificial intelligence ethical norms have become empty talk. Of course, existing philosophical analysis is not a sufficient scientific argument, so this possibility has not been proven, but it is necessary to take it seriously. Predicting and identifying this kind of risk is an extremely difficult, complex and unprecedented task, and it is related to the safety bottom line of human long-term survival.
The third risk is not serious at present, but there are certainly potential risks. Taking industrial production as an example, some labor-intensive industries have generally seen "difficulty in employment" in some areas, but this phenomenon is not caused by the application of new technologies such as artificial intelligence and robots, but by the work of a large number of positions. The nature has become a mechanical repetition of simple operations, and this kind of operation is inconsistent with human nature. The inevitable trend in the future is that fewer and fewer people are willing to undertake such work, so the demand for the application of artificial intelligence and robotics industries will become stronger and stronger, so the artificial replacement rate will become higher and higher in some industries. If the reemployment problem cannot be solved, it may cause application out of control and produce extremely serious social consequences. It can be seen that the prediction and identification of this risk is extremely complex and difficult, and requires multidisciplinary cooperation and long-term efforts.
4 Ethical innovation for major social issues
The fundamental value of artificial intelligence lies in increasing human well-being. In the AI ethical system proposed in this article, this principle is listed as the basic mission, and all ethical suggestions already proposed include this principle. A concentrated manifestation of human welfare is to help solve major problems faced by society or in the future, such as: climate warming, environmental pollution, population aging, uneven resource distribution, unbalanced economic development, and less-humanized industries.
These major social problems have three basic characteristics: First, from a nature perspective, the existing commercialization mechanism is not suitable for solving such problems; Second, there are no other effective response methods at present; Third, the solution to such problems Solutions are often not purely technical, but comprehensive, and artificial intelligence technology can play an important role in it. So, how can artificial intelligence ethics play an important role in solving major social problems? At present, the study of this issue is the weakest and most lacking link in the construction of the entire artificial intelligence ethics [19].
This article believes that the "ethical research" department in the artificial intelligence ethics system should include two basic functions. One is the "risk prediction judgment" proposed above, and the other is "ethical innovation". As a new mechanism, ethical innovation will provide research support for the response to major social problems, and its main work tasks are as follows.
First, the collection and analysis of subjective and objective data on social changes. In an era of rapid development of science and technology and industrial innovation, people's life, work and psychological state are also changing rapidly, and the subjective feelings, educational concepts, employment tendencies, consumption concepts, life attitudes and human-machine relationship cognition of different groups are also also In a constant change. At present, society has very limited grasp of this information. This situation is very unfavorable to the healthy development of society and needs to be changed urgently. Therefore, we develop corresponding artificial intelligence and big data technologies to collect indicator data that reflect these changes in a timely and fully integrate them with traditional industrial and social statistical data to obtain scientific judgments on social conditions through systematic analysis, and maintain the scientific judgment of the social situation. The smooth operation of society and the more reasonable policy decisions and planning are of great practical significance, and it also lays the necessary foundation for better response to major social problems.
Second, analysis and prediction of possible social development trends. At some time in the future, it is entirely possible that a large number of work will be replaced by machines and a large number of working-age populations have no work to do. The social structure, economic operation mechanism and social development momentum in this situation are fundamentally different from the current society. Therefore, in the process of dealing with certain major social problems, human beings are likely to enter a new stage of social civilization in the future. In order to ensure that this social evolution is in line with the fundamental interests of mankind and ensure the harmonious coexistence of all things in the universe, it is entirely necessary for mankind to prepare for the future and not passively follow the trend. Analyzing and predicting the possible trends of future social development is a necessary basis for long-term social development planning. This kind of analytical prediction is very difficult and requires multidisciplinary cooperation, where artificial intelligence technology can play an important role.
Third, innovative design of solutions to major social problems. The major social problems faced by mankind are often difficult to solve on the matter, and it is necessary to find a way to resolve them through comprehensive innovation [20]. However, in the face of such a high-dimensional and complex problem, it is impossible to solve it automatically by relying solely on artificial intelligence technology and other related technical means. Therefore, it is necessary to explore the solution mode of human-computer cooperation, and artificial intelligence technology can significantly improve the level and performance of human-computer cooperation problems. For example, using the "hypothesis reasoning" method in the "violence method" of artificial intelligence [21], human-computer cooperative problem can be solved, and there have been successful cases in high-dimensional complex application scenarios. Assuming reasoning finds that relying solely on people or An effective solution that cannot be discovered by machines. Therefore, in response to major social problems, it is possible to discover comprehensive innovative solutions that could not be discovered in the past through human-computer cooperation. In the future era of science and technology and industrial revolution, this will be a huge contribution made by the artificial intelligence ethics system to mankind.
5 Conclusion
Based on the basic consensus reached by the ethical standards of artificial intelligence, this paper proposes the planning of the ethical system of artificial intelligence, focusing on solving four key issues that ethical standards cannot be answered but the ethical system must solve - operating mechanism issues, scenario implementation issues, and risks Predict and identify problems and development momentum problems, and propose preliminary solutions to these problems.
The operating mechanism of the artificial intelligence ethical system is determined by its infrastructure, which stipulates the main departments of the ethical system and their interrelationships, including the mechanism for the implementation of the scenario. This article suggests that a new research department, ethical research, is added to the artificial intelligence innovation ecosystem, has two basic functions: artificial intelligence risk prediction and judgment and ethical innovation in dealing with major social problems. According to these analysis and suggestions, in the future era of artificial intelligence, social progress and economic development will enter a "two-wheel drive" model, with traditional commercial innovation and newly established ethical innovation as two different and interrelated driving mechanisms.
In short, the construction of artificial intelligence ethics faces a series of challenges, and it cannot be effective by concreting general ethical principles, methods and rules into artificial intelligence. How to establish such an artificial intelligence ethics system still requires close cooperation among relevant parties and long-term and arduous exploration.
Acknowledgements
The author has benefited a lot from the relevant exchanges with the following scholars and professionals: Academician Li Deyi, Zhao Tingyang, Chen Jiaying, Wang Rongrong, Song Xiaogang, Hao Yucheng, Yu Jian, Wang Weining, Pan Tianyou, Qin Yu, van den Hoven, Liu Xiaoli, Su Yanjie, Sun Zhouxing, Wang Guoyu, Song Bing, Liu Zhe, Liang Zheng, Steve Angle.




